Introduction
Very often DBAs need to find the location of the physical file (MDF, LDF & NDF) of a database. Simply we can obtain the output by executing the below query. Run the script to get the SQL Server database file location for all the databases for a particular instance.
Retrieving Database File Details Using T-SQL
In SQL Server, obtaining detailed information about your databases and their associated files can be crucial for effective management and maintenance. This blog post will guide you through a T-SQL script that fetches comprehensive details about the database files on your server. This script, authored by Soyeluddin Biswas, leverages system views and dynamic management views to provide valuable insights into the file size, location, and usage.
Script to find the physical file location
-- T-SQL Author: Soyeluddin Biswas
-- Website: https://ourtechideas.com/
-- Created Date: 25 September 2019
-- Declare and set the server name
DECLARE @ServerName NVARCHAR(128)
SET @ServerName = CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName') AS NVARCHAR(128))
-- Retrieve the database file details
SELECT
@ServerName AS [Server Name], -- Server name
d.name AS [Database Name], -- Database name
d.database_id AS [Database ID], -- Database ID
f.name AS [Physical File Type], -- Type of the physical file
f.physical_name AS [Physical File Location], -- Location of the physical file
f.state_desc AS [Online Status], -- Online status of the file
f.size * 8.00 * 1024.00 AS [Size In Bytes], -- Size of the file in bytes
CAST((f.size * 8.00 * 1024.00) / 1048576.00 AS NUMERIC(18,2)) AS [Size In MB], -- Size of the file in megabytes
CAST((f.size * 8.00 * 1024.00) / 1073741824.00 AS NUMERIC(18,2)) AS [Size In GB], -- Size of the file in gigabytes
CAST((f.size * 8.00 * 1024.00) / 1099511627776.00 AS NUMERIC(18,2)) AS [Size In TB], -- Size of the file in terabytes
CAST(CAST(v.total_bytes - v.available_bytes AS FLOAT) / CAST(v.total_bytes AS FLOAT) * 100 AS NUMERIC(18,2)) AS [Used Disk Percent] -- Percentage of disk space used by the file
FROM
sys.master_files f
INNER JOIN sys.databases d ON d.database_id = f.database_id
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_os_volume_stats(f.database_id, f.file_id) v
ORDER BY
--d.database_id -- Sort by database ID
[Size In GB] DESC -- Sort by size in gigabytes in descending order
Result
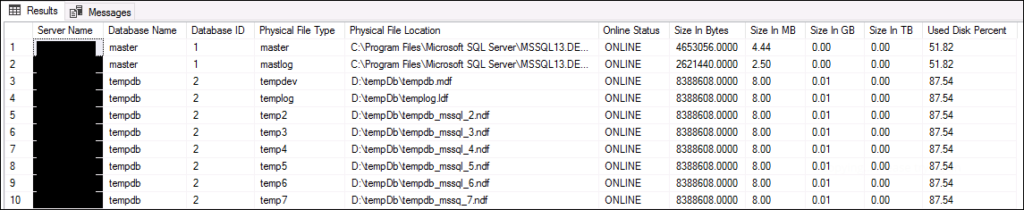
Why This Script is Useful
This script is particularly beneficial for database administrators and developers who need to monitor and manage the storage of SQL Server databases. It provides a quick overview of:
- The size of each database file.
- The physical location of these files.
- Their online status.
- The percentage of used disk space.
By having this information readily available, you can make informed decisions about disk space management, database growth, and file optimization.
Conclusion
Managing SQL Server databases effectively requires insight into the underlying files and their usage. This T-SQL script, provided by Soyeluddin Biswas, offers a robust solution to gather essential details about your database files. By understanding and utilizing this script, you can ensure better database performance and efficient storage management.
For more insights and scripts related to SQL Server and other technologies, visit Our Tech Ideas.
Feel free to adapt and expand this script to suit your specific needs and scenarios. Happy querying!
