Introduction
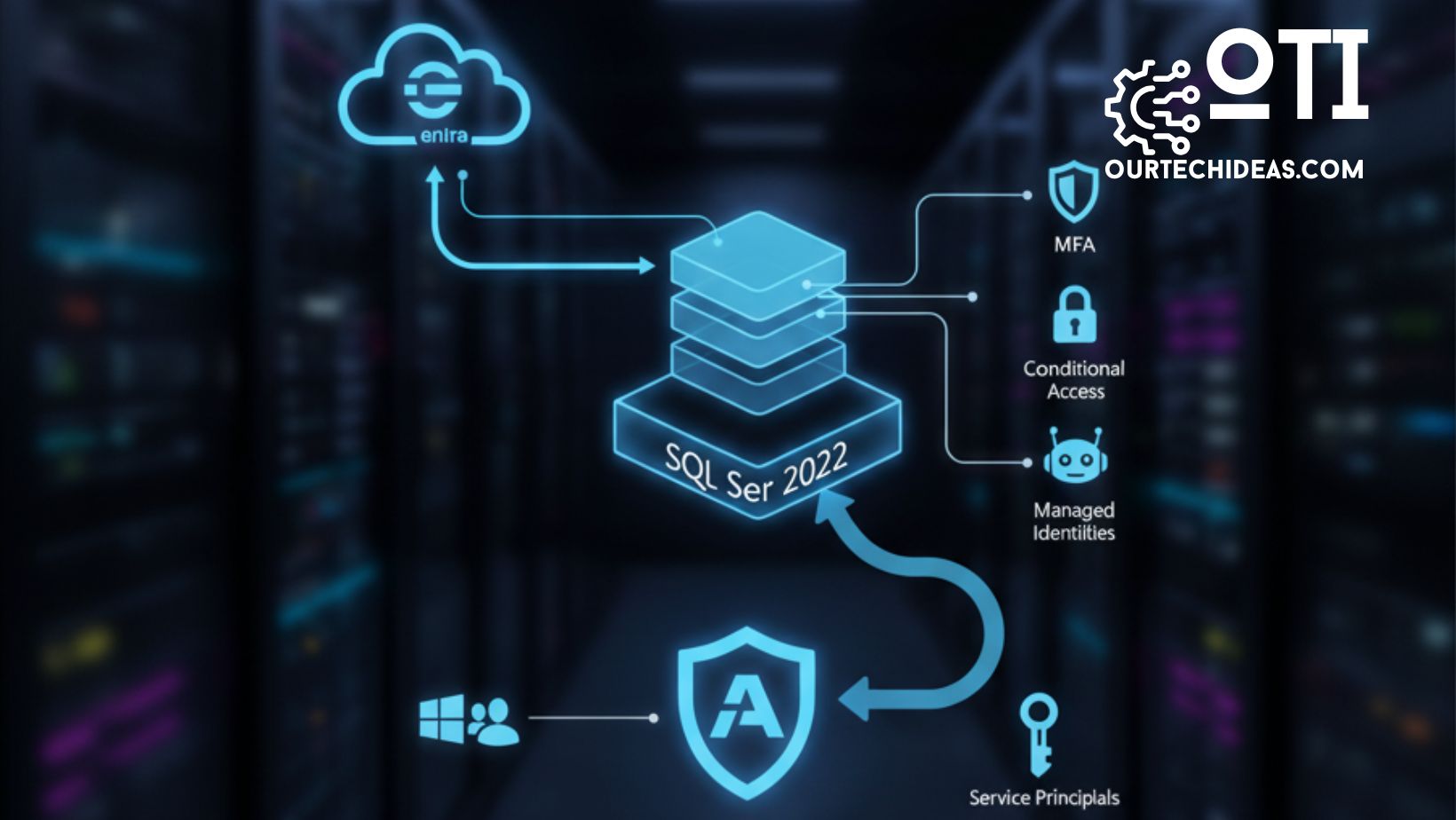
With the advancement of cloud-native technology and hybrid workloads, secure database access has become more important—and more complex—than ever. Traditionally, SQL Server supported Windows authentication and SQL authentication for user management and access control. SQL Server 2022 ushers in a new era by introducing Microsoft Entra ID authentication (formerly Azure AD authentication), enabling organizations to unify and modernize their identity and security strategies.
What is Microsoft Entra ID Authentication in SQL Server?
Microsoft Entra authentication allows SQL Server to use Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) for login and access management, extending the cloud-powered identity management capabilities once limited to Azure SQL databases, Azure SQL Managed Instances, and Synapse Analytics to on-premises and hybrid SQL Server deployments.
This authentication mode lets you:
- Use user and group identities from Microsoft Entra ID,
- Leverage managed identities and service principals,
- Gain features such as multifactor authentication (MFA), passwordless logins, conditional access, and centralized policy management.
Multiple authentication methods are supported, including integrated (SSO), username and password, service principals, managed identities, and access tokens.
Windows, SQL, and Microsoft Entra Authentication: Key Differences
| Feature | Windows Authentication | SQL Authentication | Microsoft Entra Authentication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identity Source | Windows AD | SQL Server (internal login) | Microsoft Entra ID (cloud/federated identities) |
| Security Model | Kerberos/NTLM, SSO | Username/password, policies | Conditional access, MFA, passwordless, RBAC |
| Use Cases | On-premises, domain users | Legacy or cross-platform, isolated | Cloud/hybrid, managed identities, automation |
| Centralized Policy Management | GPO and AD | Per-server | Microsoft Entra Admin Console |
| Automation/DevOps Friendly | Limited | Partial | Yes (service principal, managed identity) |
| Modern Security Controls | No | No | Yes (MFA, risk-based policies, passwordless) |
- Windows authentication is best suited for traditional, domain-joined environments, offering integrated SSO and strong security but limited to on-premises or hybrid domains.
- SQL authentication (username/password within SQL Server) helps with cross-platform access and legacy support but provides less centralized control and potentially weaker security.
- Microsoft Entra authentication centralizes identity, supports modern zero-trust security features, and integrates seamlessly with Azure services, making it ideal for today’s hybrid and cloud-first workloads.
How to Configure Microsoft Entra Authentication in SQL Server
To enable and use Microsoft Entra authentication—
- Connect your SQL Server to Azure Arc (for on-premises environments) or ensure SQL Server on Azure VMs is registered with IaaS Agent Extension.
- Register your required Microsoft Entra ID users, groups, or managed identities.
- Set a Microsoft Entra administrator for your SQL instance via the Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
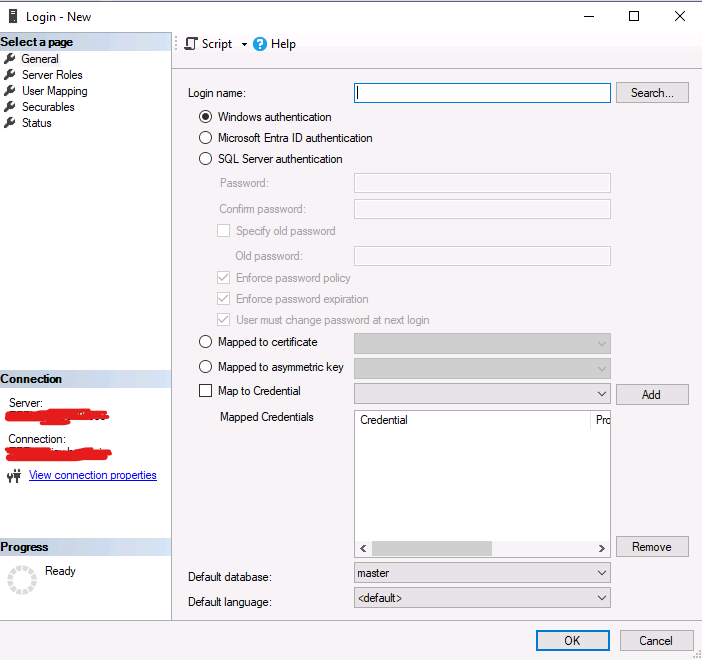
- Create logins and users in SQL Server referencing the corresponding Entra identities.
- Leverage supported authentication methods (integrated, password, managed identity, etc.).
- Assign appropriate roles and permissions using role-based access control (RBAC) and best practices.
Example: Creating a Contained Database User
CREATE USER [username@domain.com] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;This creates a user in the database mapped to a Microsoft Entra ID identity.
When to Use Microsoft Entra Authentication
Adopt Microsoft Entra authentication when:
- Environments span on-premises, cloud, and hybrid workloads.
- Centralized, cloud-based identity management and single sign-on are required.
- There is a need for advanced security features (MFA, conditional access, etc.).
- Applications leverage managed identities or service principals (for automation/DevOps scenarios).
- Compliance or audit requires robust security and centralized control.
It is especially recommended for organizations leveraging Azure, operating hybrid networks, or gradually migrating from on-premises AD to modern cloud-based solutions.
Benefits and Considerations
Key Benefits
- Centralized management of all identities (users, groups, apps).
- Advanced security with MFA, conditional access, passwordless authentication.
- Seamless hybrid support and policy enforcement.
- Automation and DevOps friendly via service principals and managed identities.
Important Considerations
- Not all legacy and isolated systems are compatible.
- Requires proper registration and configuration in Azure and SQL Server.
- Service accounts and some AD-specific features may not be directly supported; assess use cases before shifting critical workloads.
Conclusion
Microsoft Entra authentication marks a significant step forward in secure, modern database access for SQL Server—bridging on-premises, hybrid, and cloud environments with centralized, policy-driven identity and security. For organizations modernizing infrastructure or adopting zero-trust, Entra authentication is quickly becoming the default for future-proofing SQL Server deployments.
References:
- Microsoft Entra authentication for SQL Server overview
- Configure and manage Microsoft Entra authentication with Azure SQL
This approach will help organizations and DBAs improve security and simplify management while preparing for future workloads and compliance demands.